Amps to Watts Converter
Is this tool helpful?
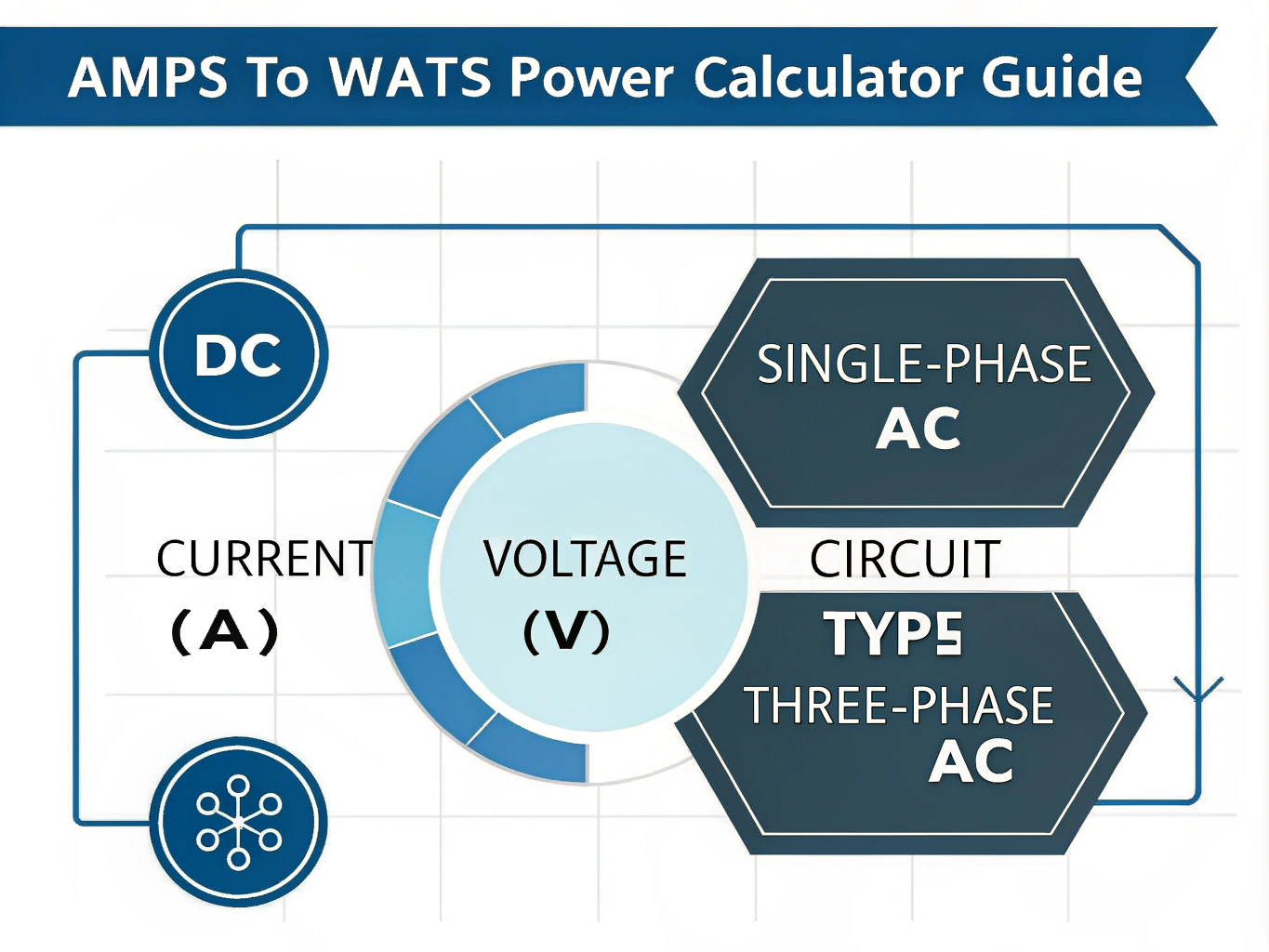
How to Use the Amps to Watts Converter Effectively
Use this calculator to quickly convert electrical current (amperes) and voltage (volts) into power (watts) based on your circuit type. Follow these steps:
- Enter Current (A): Input the electrical current in amperes. For example, enter 3.5 A for a small appliance or 12 A for a power tool.
- Enter Voltage (V): Provide the voltage in volts. Examples include 110 V for some household electronics or 400 V for industrial equipment.
- Select Circuit Type: Choose one of the following based on your electrical system:
- DC Circuit – Common for batteries and solar panels
- Single-Phase AC Circuit – Typical in residential settings
- Three-Phase AC Circuit – Used in factories and heavy machinery
- Power Factor (for AC circuits): This optional field appears when you select an AC circuit. Enter a value between 0 and 1 to reflect how efficiently your AC equipment uses power. For example, enter 0.9 for an office computer or 0.75 for an industrial motor.
Understanding the Amps to Watts Converter: Purpose and Benefits
This tool helps you calculate the electrical power consumption or output by converting measurements of current and voltage. It supports direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) circuits, including single-phase and three-phase systems. By entering accurate values, you get precise wattage calculations instantly, removing the chance of manual errors.
- Simple Power Calculation: Convert current and voltage values into watts quickly.
- Multiple Circuit Types: Works for DC, single-phase AC, and three-phase AC electrical systems.
- Power Factor Inclusion: Accounts for power factor in AC circuits, improving accuracy.
- Energy Management: Use the output for monitoring energy use, sizing electrical components, or optimizing system performance.
Mathematical Formulas Behind the Converter
The tool uses these formulas to determine power in watts (W) depending on the selected circuit type.
DC Circuits
Power is the product of voltage and current:
$$P = V \times I$$Single-Phase AC Circuits
Power includes the power factor (PF), which reflects how efficiently the load uses power:
$$P = V \times I \times PF$$Three-Phase AC Circuits
For three-phase systems, the square root of 3 (√3) accounts for phase relationships:
$$P = \sqrt{3} \times V \times I \times PF$$- P = Power in watts (W)
- V = Voltage in volts (V)
- I = Current in amperes (A)
- PF = Power Factor (between 0 and 1, for AC circuits)
Example Calculations Demonstrating the Amps to Watts Tool
Example 1: DC Circuit
- Current = 7 A
- Voltage = 24 V
- Circuit Type = DC Circuit
- Power = 7 × 24 = 168 watts
Example 2: Single-Phase AC Circuit
- Current = 10 A
- Voltage = 220 V
- Power Factor = 0.85
- Power = 10 × 220 × 0.85 = 1,870 watts
Example 3: Three-Phase AC Circuit
- Current = 18 A
- Voltage = 415 V
- Power Factor = 0.9
- Power = √3 × 18 × 415 × 0.9 ≈ 11,651 watts
Key Advantages of Using the Amps to Watts Converter
- Fast and Accurate Calculations: Quickly get reliable power measurements based on your inputs.
- Supports Multiple Electrical Systems: Covers DC and various AC circuit types, making it versatile for different applications.
- Includes Power Factor Impact: Accounts for real-world AC circuit efficiency to produce accurate wattage.
- Enhances Energy Management: Facilitates better planning, energy use monitoring, and electrical system design.
- Educational Tool: Helps you understand how current, voltage, and power interrelate in electrical circuits.
Practical Uses and Applications of the Amps to Watts Converter
Household Appliance Power Assessment
Calculate the power consumption of devices like refrigerators, air conditioners, or lighting systems. This helps you estimate energy costs and manage your electrical loads.
Solar Power System Design
Determine the output power of solar panels and battery charging rates by converting current and voltage readings accurately.
Industrial Equipment Monitoring
Use the tool to calculate power consumption in motors, pumps, and machinery to optimize energy efficiency and plan maintenance.
Electrical Panel and Circuit Sizing
Estimate total power requirements to select appropriate circuit breakers, wiring, and panel capacity, ensuring safety and compliance with electrical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions About Amps to Watts Conversion
What is the power factor and why does it matter?
The power factor indicates how efficiently your AC equipment uses electricity. It is a number between 0 and 1. A higher power factor means more efficient power use and less wasted energy.
Why does the three-phase power calculation include the √3 factor?
Three-phase systems have voltages and currents out of phase by 120 degrees, so multiplying by √3 balances these relationships to calculate total power accurately.
When should I choose DC over AC calculations?
Choose DC calculations for battery-powered devices, solar panel systems, and DC power supplies. Select AC calculations for household wiring, utility power, and industrial setups.
How do I find the power factor for my electrical equipment?
Typical power factors are:
- Resistive loads (e.g., heaters): close to 1.0
- Electric motors: around 0.8 to 0.85
- Lighting systems such as fluorescents: 0.95 to 0.98
Can I use this calculator for sizing electrical panels?
Yes. It helps determine total power demand, which is essential for selecting the right panel capacity and circuit breaker sizes.
How does voltage influence power calculation?
Voltage directly impacts power. Increasing voltage with the same current increases power proportionally. Understanding this helps in system design and optimizing energy use.
Important Disclaimer
The calculations, results, and content provided by our tools are not guaranteed to be accurate, complete, or reliable. Users are responsible for verifying and interpreting the results. Our content and tools may contain errors, biases, or inconsistencies. Do not enter personal data, sensitive information, or personally identifiable information in our web forms or tools. Such data entry violates our terms of service and may result in unauthorized disclosure to third parties. We reserve the right to save inputs and outputs from our tools for the purposes of error debugging, bias identification, and performance improvement. External companies providing AI models used in our tools may also save and process data in accordance with their own policies. By using our tools, you consent to this data collection and processing. We reserve the right to limit the usage of our tools based on current usability factors.