Customer Lifetime Value Predictor
Is this tool helpful?
How to Use the Customer Lifetime Value Calculator Effectively
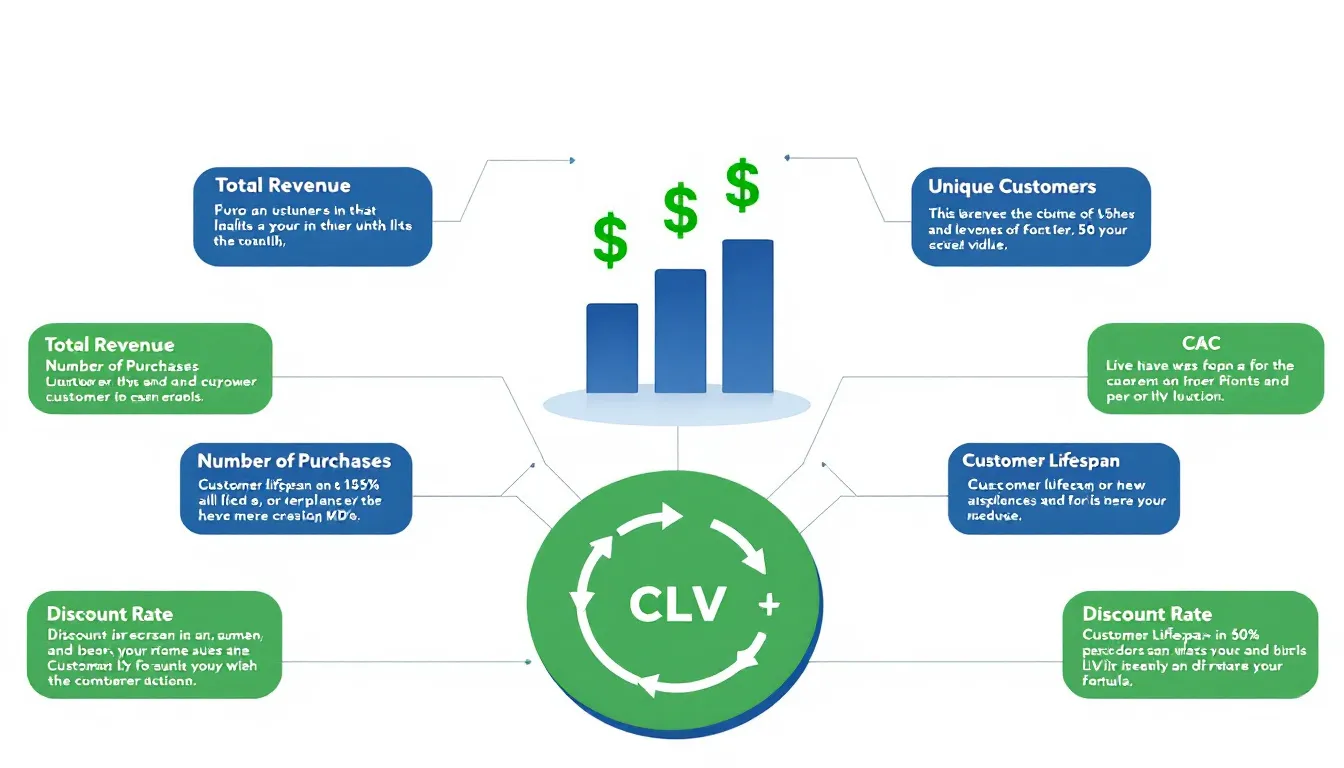
Use this Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Calculator to estimate the total value your customers bring to your business over time. Here’s how to fill out each field accurately, with sample inputs to guide you:
- Total Revenue: Enter the total revenue generated during a specific period. For example, if your sales reached $150,000 last quarter, input 150000. Or, for a six-month period with $90,000 revenue, input 90000.
- Number of Purchases: Input the total number of transactions in that period. If you processed 3,000 sales last quarter, enter 3000. If you had 1,800 transactions over six months, input 1800.
- Number of Unique Customers: Provide the count of distinct customers who purchased. For instance, if 1,200 individual customers made purchases last quarter, enter 1200. For 700 customers over six months, input 700.
- Average Customer Lifespan (months): Enter how long customers typically stay active, measured in months. If your customers stay an average of 18 months, input 18. For two years, input 24.
- Discount Rate (%) (Optional): If you want to adjust for the time value of money, enter a discount rate. For example, use 6 for a 6% rate or 4.5 for 4.5%. Leave blank if not applicable.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) (Optional): Input your average cost to acquire a customer. If you spend $120 per customer, enter 120. For $75 acquisition cost, enter 75. Leave blank if unknown.
Once these fields are complete, click “Calculate CLV” to see detailed metrics, including your Average Purchase Value, Purchase Frequency Rate, Customer Value, Lifetime Value, Discounted CLV, and CLV to CAC Ratio.
An Introduction to the Customer Lifetime Value Calculator: Definition, Purpose, and Benefits
The Customer Lifetime Value Calculator estimates how much a customer contributes financially throughout their entire relationship with your business. This helps you focus on retention, optimize your marketing spend, and increase profits.
What is Customer Lifetime Value?
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) measures the total revenue you expect from a single customer over the entire duration they do business with you. It combines purchase patterns, buying frequency, and expected customer lifespan.
The core formula for CLV is:
Where Customer Value is:
Purpose of Calculating Customer Lifetime Value
Calculating CLV gives you insights to:
- Allocate marketing budgets wisely
- Improve customer segmentation and targeting
- Develop strategies to increase customer retention
- Justify spending on acquiring new customers
- Forecast future revenue and growth opportunities
Benefits of Using the Customer Lifetime Value Calculator
This calculator provides many advantages to help grow your business:
- Data-Driven Insights: Understand the true value of your customers for better planning.
- Targeted Marketing: Prioritize high-value customers to maximize ROI on campaigns.
- Optimized Spending: Spend just the right amount on acquisition and retention to remain profitable.
- Improved Customer Experience: Invest in service and loyalty efforts knowing their long-term impact.
- Accurate Revenue Forecasting: Use CLV for precise long-range financial modeling.
Example Calculations Using the Customer Lifetime Value Calculator
Here’s an example showing how this JavaScript-based CLV Calculator handles your inputs and delivers results:
Sample Business Data
- Total Revenue: $350,000
- Number of Purchases: 5,000
- Number of Unique Customers: 1,400
- Average Customer Lifespan: 20 months
- Discount Rate: 5%
- Customer Acquisition Cost: $100
Step-by-Step Calculations
- Average Purchase Value: $$\frac{350,000}{5,000} = 70$$
- Average Purchase Frequency Rate: $$\frac{5,000}{1,400} \approx 3.57$$ purchases per customer
- Customer Value: $$70 \times 3.57 = 249.9$$
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): $$249.9 \times 20 = 4,998$$
- Discounted CLV (using discounted cash flow): approximately $$4,330.20$$
- CLV to CAC Ratio: $$\frac{4,998}{100} = 49.98$$
This example demonstrates how the calculator quickly provides detailed insights that guide your marketing and retention strategies.
How the Customer Lifetime Value Calculator Solves Key Business Challenges
1. Simplifies Complex Calculations
Calculating CLV can be complicated. This tool does the math for you once you enter basic revenue and customer data, making it easy to get accurate results without spreadsheets or manual formulas.
2. Accounts for Time Value of Money
By allowing an optional discount rate, the calculator reflects the true present value of future customer revenue:
Where:
- t = time period (months)
- n = average customer lifespan (months)
3. Evaluates Customer Acquisition Efficiency
Including Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) lets you calculate the CLV to CAC Ratio, which indicates if your customer acquisition spending is profitable:
- A ratio over 1 means customers generate more value than they cost to acquire.
- A ratio of 3 or higher signals efficient acquisition worthy of scaling.
- Ratios above 5 highlight opportunities to invest more in growth.
4. Supports Data-Driven Business Decisions
With a clear picture of customer value, you can:
- Allocate marketing budgets more effectively
- Identify high-potential customer segments
- Guide product and service enhancements
- Justify investment in customer service and loyalty programs
Practical Use Cases of the Customer Lifetime Value Calculator
1. Online Retailers and E-commerce Stores
- Identify which customer groups generate the most profit
- Determine how much to spend on targeted ads and promotions
- Plan loyalty rewards to extend customer lifespan and boost purchase frequency
Example Scenario:
- Total Revenue: $1,200,000
- Number of Purchases: 8,000
- Number of Unique Customers: 4,000
- Average Customer Lifespan: 30 months
- Discount Rate: 6%
- Customer Acquisition Cost: $60
2. Subscription-Based Software Companies (SaaS)
- Forecast recurring revenue based on customer retention
- Evaluate pricing models and subscription plans
- Assess churn impact on long-term revenue
Example Scenario:
- Total Revenue: $4,800,000
- Number of Purchases (renewals): 48,000
- Number of Unique Customers: 4,000
- Average Customer Lifespan: 36 months
- Discount Rate: 8%
- Customer Acquisition Cost: $400
3. Financial Services and Banking
- Analyze customer profitability across segments
- Optimize cross-selling and upselling strategies
- Adjust service levels for high-value customers
Example Scenario:
- Total Revenue: $8,000,000
- Number of Purchases (transactions): 400,000
- Number of Unique Customers: 40,000
- Average Customer Lifespan: 48 months
- Discount Rate: 7%
- Customer Acquisition Cost: $200
Use this Customer Lifetime Value Calculator to make data-driven decisions that help increase your customer retention, improve profitability, and grow your business sustainably.
Important Disclaimer
The calculations, results, and content provided by our tools are not guaranteed to be accurate, complete, or reliable. Users are responsible for verifying and interpreting the results. Our content and tools may contain errors, biases, or inconsistencies. Do not enter personal data, sensitive information, or personally identifiable information in our web forms or tools. Such data entry violates our terms of service and may result in unauthorized disclosure to third parties. We reserve the right to save inputs and outputs from our tools for the purposes of error debugging, bias identification, and performance improvement. External companies providing AI models used in our tools may also save and process data in accordance with their own policies. By using our tools, you consent to this data collection and processing. We reserve the right to limit the usage of our tools based on current usability factors.