Cylinder Volume Calculator
Is this tool helpful?
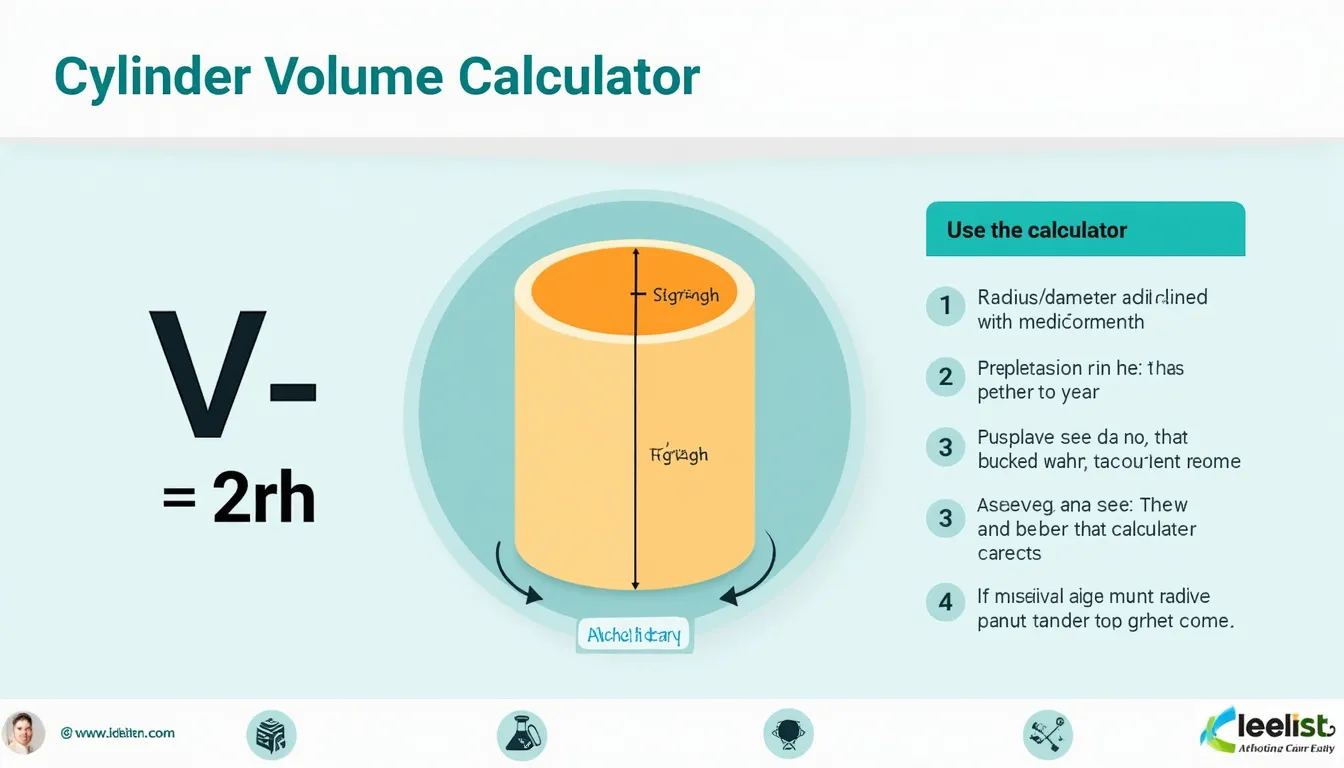
How to use the tool
- Select a measurement type—choose Radius or Diameter depending on what you know.
- Enter the base value
- Radius example: 3 cm
- Diameter example: 14 ft
- Enter the height in the same unit
- Height example with radius: 8 cm
- Height example with diameter: 6 ft
- Pick the unit—centimeters, meters, inches, or feet.
- Press “Calculate Volume” to see cubic units, liters, and U.S. gallons instantly.
Formulas used
Radius given:
$$V = \pi r^2 h$$
Diameter given:
$$V = rac{\pi d^2 h}{4}$$
Worked examples
- Example 1 – r = 3 cm, h = 8 cm
- V = π·3²·8 = 226.19 cm³
- Liters = 0.226 L
- Gallons = 0.059 gal
- Example 2 – d = 14 ft, h = 6 ft
- r = 7 ft → V = π·7²·6 = 923.63 ft³
- Liters = 26 165 L
- Gallons = 6 910 gal
Quick-Facts
- π ≈ 3.14159 (NIST DLMF, https://dlmf.nist.gov/)
- 1 ft³ = 28.3168 L (NIST, https://physics.nist.gov/)
- 1 U.S. gal = 3.78541 L (NIST, https://physics.nist.gov/)
- Standard 55-gal drum holds 208.2 L (EPA Oil Spill Guidance, https://www.epa.gov/)
- Common steel pipe diameters: 0.5-48 in (ANSI/ASME B36.10M-2018)
What is cylinder volume?
Cylinder volume is the three-dimensional space inside a right circular cylinder, calculated from base area and height (ISO 80000-3).
Which formula does the calculator use?
It applies $$V=\pi r^{2}h$$ for radius inputs or $$V= rac{\pi d^{2}h}{4}$$ for diameter inputs (DLMF, https://dlmf.nist.gov/).
How accurate are the results?
The tool keeps π to 15 digits, giving sub-milliliter accuracy for liter outputs (NIST, https://physics.nist.gov/).
Can I mix units?
No. Base and height must share a unit; mixing produces dimensional errors (ISO 80000-1).
How do I turn cm³ into liters?
Divide by 1 000 because 1 L = 1 000 cm³ (NIST, https://physics.nist.gov/).
Why does cylinder volume matter in industry?
Engineers size tanks, pipes, and drums by volume to ensure capacity and safety (API 650). “Accurate volume calculations are critical for containment integrity” (API Standard 650-2020).
Radius vs diameter—what’s faster?
Entering radius avoids the rac{d}{2} step, but both give identical results when done correctly (MathWorld Cylinder, https://mathworld.wolfram.com/).
Common mistakes to avoid?
- Mixing inches and feet.
- Typing diameter into the radius field.
- Forgetting to convert ft³ to gallons.
Important Disclaimer
The calculations, results, and content provided by our tools are not guaranteed to be accurate, complete, or reliable. Users are responsible for verifying and interpreting the results. Our content and tools may contain errors, biases, or inconsistencies. Do not enter personal data, sensitive information, or personally identifiable information in our web forms or tools. Such data entry violates our terms of service and may result in unauthorized disclosure to third parties. We reserve the right to save inputs and outputs from our tools for the purposes of error debugging, bias identification, and performance improvement. External companies providing AI models used in our tools may also save and process data in accordance with their own policies. By using our tools, you consent to this data collection and processing. We reserve the right to limit the usage of our tools based on current usability factors.