Is this tool helpful?
How to Use the Revenue per Employee Calculator Effectively
This comprehensive revenue per employee calculator helps analyze your company’s operational efficiency through three simple steps:
- Step 1: Enter your company’s annual revenue in USD (e.g., $5,750,000 or $12,450,000)
- Step 2: Input the total number of full-time employees (FTE) (e.g., 25 or 47)
- Step 3: Select your industry from the dropdown menu (Technology, Finance, Retail, or Manufacturing)
The calculator will instantly provide your revenue per employee, compare it to industry averages, and show your performance relative to the industry benchmark.
Understanding Revenue per Employee Analysis
Revenue per employee is a crucial metric that measures how efficiently a company generates revenue through its workforce. The formula for this calculation is:
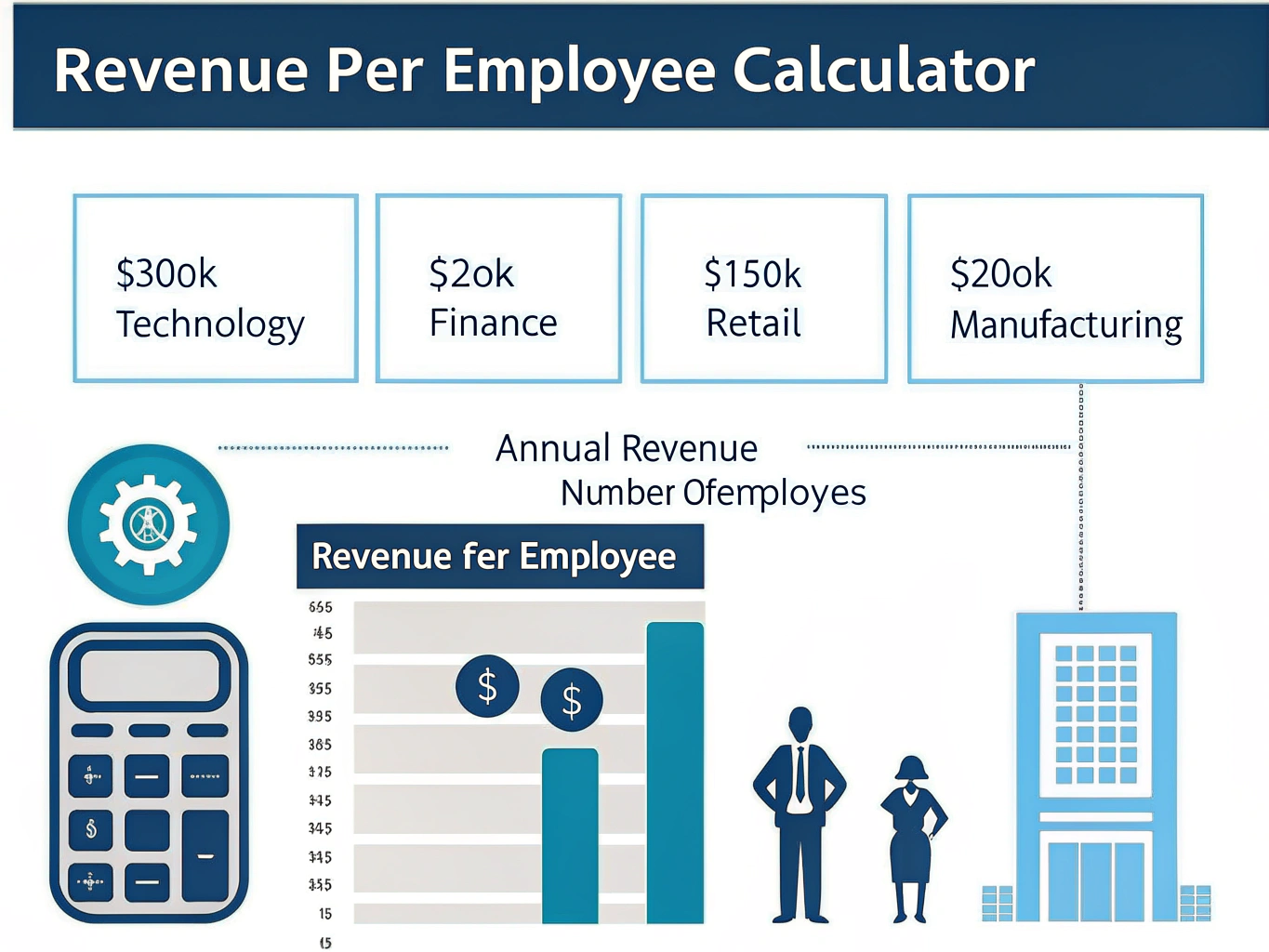
$$ \text{Revenue per Employee} = \frac{\text{Annual Revenue}}{\text{Number of Full-Time Employees}} $$This metric serves as a key performance indicator (KPI) for operational efficiency and productivity across different business sectors.
Industry Benchmarks
Different industries have varying revenue per employee benchmarks:
- Technology: $300,000 per employee
- Finance: $250,000 per employee
- Retail: $150,000 per employee
- Manufacturing: $200,000 per employee
Benefits of Using the Revenue per Employee Calculator
1. Strategic Decision Making
- Identify operational inefficiencies
- Guide hiring decisions
- Support resource allocation
- Benchmark against competitors
2. Performance Monitoring
- Track productivity trends
- Measure organizational efficiency
- Evaluate business model effectiveness
- Monitor growth sustainability
3. Business Planning
- Optimize workforce planning
- Guide expansion strategies
- Support budget allocation
- Enhance investment decisions
Practical Applications and Problem Solving
Case Study 1: Technology Startup
Consider a growing tech startup with annual revenue of $8,400,000 and 24 employees. Using the calculator:
- Revenue per Employee = $8,400,000 ÷ 24 = $350,000
- Comparison to Industry Average: 16.7% above technology sector average
- Indicates strong operational efficiency and scalable business model
Case Study 2: Retail Chain
A retail business generating $4,500,000 annually with 35 employees:
- Revenue per Employee = $4,500,000 ÷ 35 = $128,571
- Comparison to Industry Average: 14.3% below retail sector average
- Suggests need for operational optimization or process improvement
Strategic Implementation Guidelines
1. Performance Optimization
- Regular monitoring of revenue per employee trends
- Implementation of efficiency improvement programs
- Development of productivity enhancement strategies
2. Resource Management
- Balanced workforce planning
- Strategic hiring decisions
- Optimal resource allocation
3. Growth Planning
- Scaling strategies development
- Market expansion analysis
- Investment planning optimization
Industry-Specific Considerations
Technology Sector
High revenue per employee expectations due to:
- Scalable digital products
- Automation capabilities
- High-value intellectual property
Financial Services
Moderate to high revenue per employee driven by:
- High-value transactions
- Specialized expertise
- Complex service offerings
Retail Sector
Lower revenue per employee due to:
- Labor-intensive operations
- Lower profit margins
- High employee count requirements
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good revenue per employee ratio?
A good ratio varies by industry. Technology companies typically aim for $300,000 or higher, while retail businesses might target $150,000 per employee. The key is to compare your performance against industry-specific benchmarks.
How often should I calculate revenue per employee?
Best practice is to calculate this metric quarterly or annually to track trends and make informed decisions about hiring, resource allocation, and operational efficiency.
Can this metric help with hiring decisions?
Yes, revenue per employee helps determine if adding staff will maintain or improve operational efficiency. It provides insights into optimal staffing levels for your business model.
Should part-time employees be included in the calculation?
Convert part-time employees to full-time equivalents (FTE) for accurate calculations. For example, two half-time employees equal one FTE.
How can I improve my revenue per employee ratio?
Improvement strategies include:
- Implementing automation and efficiency tools
- Optimizing business processes
- Providing employee training and development
- Focusing on high-value products or services
- Streamlining operations and reducing redundancies
Does company size affect the revenue per employee metric?
Yes, companies of different sizes may have varying revenue per employee ratios due to economies of scale, operational efficiency, and business model differences. Compare with similar-sized companies in your industry for meaningful insights.
Important Disclaimer
The calculations, results, and content provided by our tools are not guaranteed to be accurate, complete, or reliable. Users are responsible for verifying and interpreting the results. Our content and tools may contain errors, biases, or inconsistencies. We reserve the right to save inputs and outputs from our tools for the purposes of error debugging, bias identification, and performance improvement. External companies providing AI models used in our tools may also save and process data in accordance with their own policies. By using our tools, you consent to this data collection and processing. We reserve the right to limit the usage of our tools based on current usability factors. By using our tools, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and agreed to this disclaimer. You accept the inherent risks and limitations associated with the use of our tools and services.